Appearance
Loops
A loop is a way to repeat an action multiple times without having to write it out each time. Instead of doing the same thing over and over manually, loops automate the repetition for you.
WeWeb offers two types of loops for handling repetitive actions in your workflows: Iterator (for loop) and While.
Iterator (for loop)
An Iterator is like a helper that repeats an action for each item in a list. You pass a list of data and it automatically performs the same action on each item, one after another, until it has processed every item in your list.
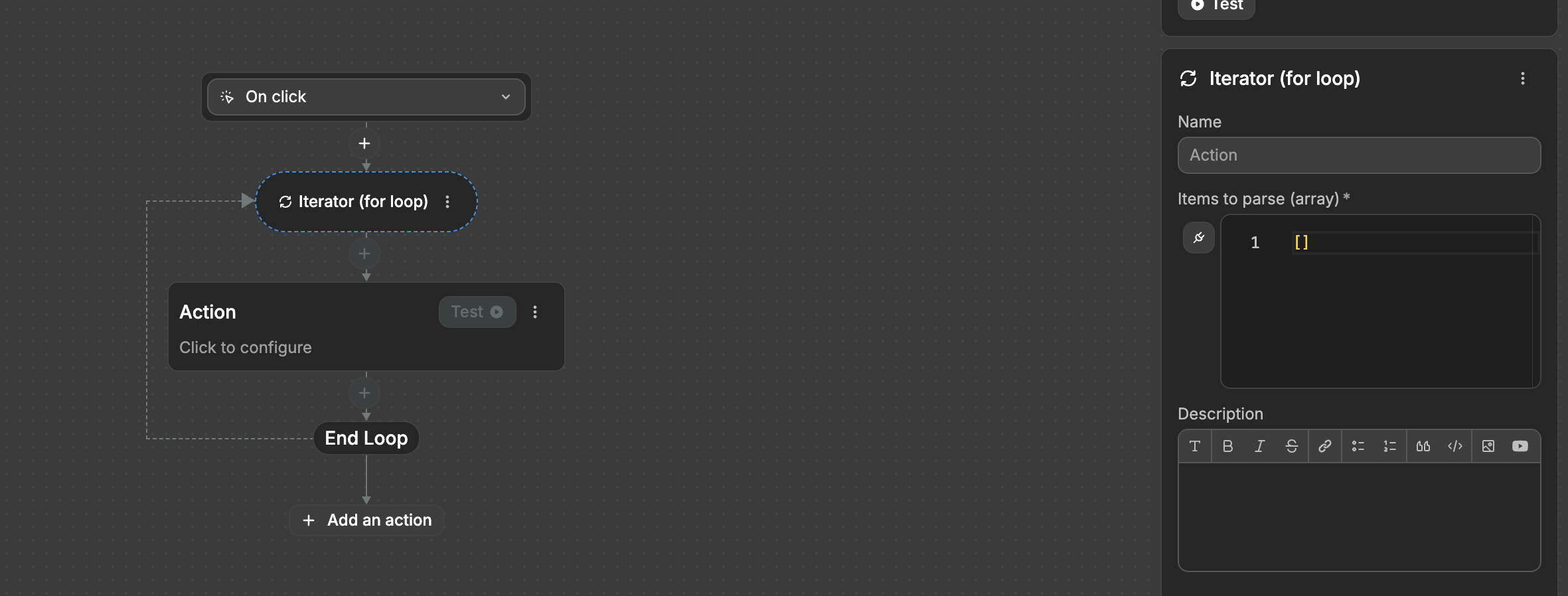
Example:
Imagine building a travel planning app. A user types in three cities they want to visit: "Paris", "London" and "Tokyo"
To show these cities on a map, you need their exact coordinates. A city name alone isn't enough - maps need numbers like (48.8566, 2.3522) for Paris. So your Iterator would:
- Take "Paris" first
- Ask a geocoding API "what are the coordinates for Paris?"
- Put a pin on the map at those coordinates
- Move on to "London" and do the same thing
- Finally handle "Tokyo"
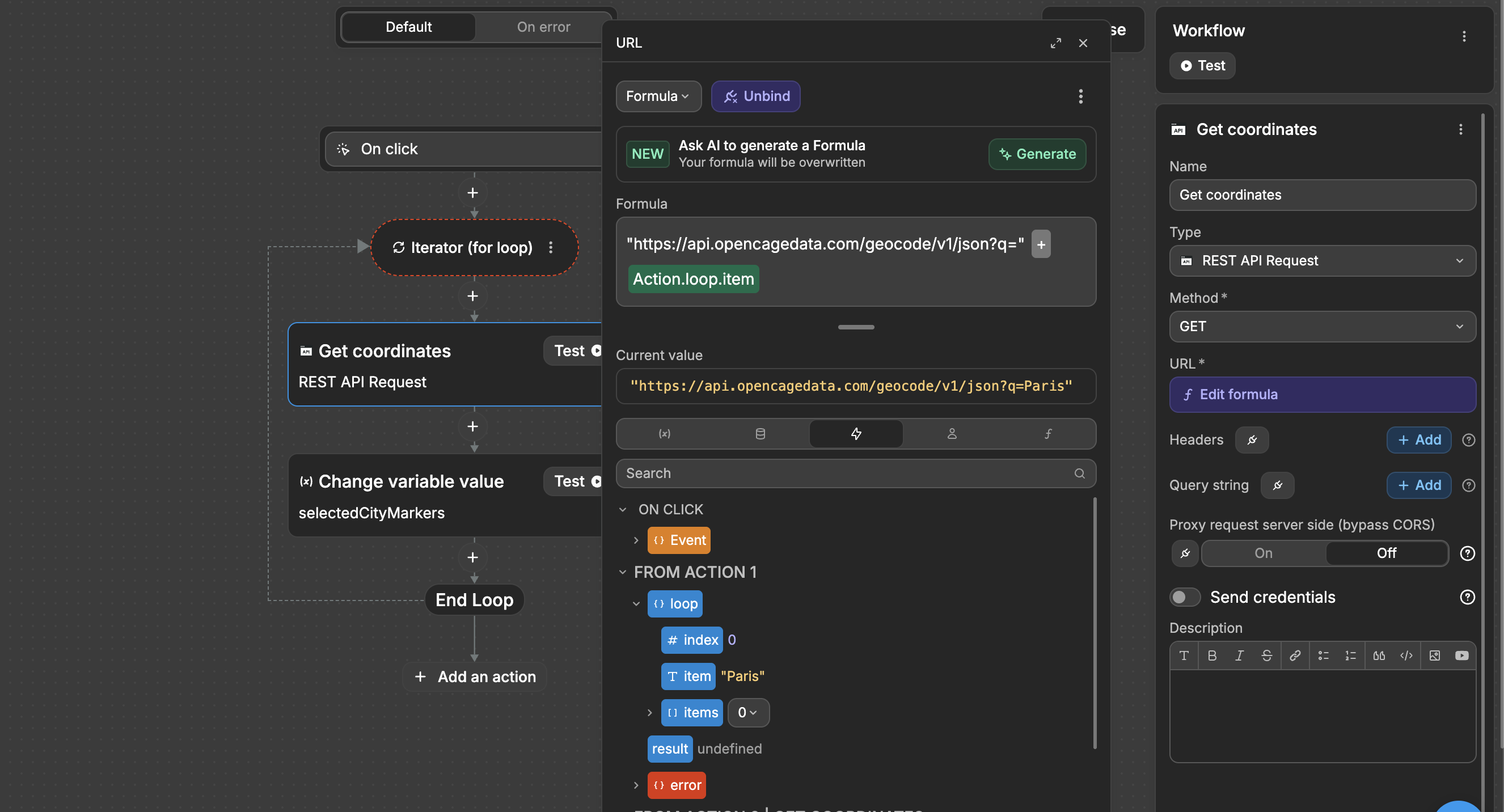
In the example above, you can see that:
- We loop through a list of city names
- Based on the current item we are looping through which can be accessed through the
Eventstab, we make a dynamic API call to OpenCage to get the coordinates of the city - We update a
selectedCityMarkersvariable that we will then bind to our map element to display markers on the selected cities
Without an Iterator, you'd need to do this manually for each city. The Iterator automates this repetitive process, handling each city in your list one after another.
In the video below, we demonstrate how to configure an Iterator to get coordinates for multiple cities using an API call in more detail:
TIP
The video demo shows getting city coordinates, but you can apply this same pattern to any scenario where you need to process a list of items one by one.
Accessing loop information
Inside an Iterator loop, you can access information about the current iteration through the Events tab. Click on the Events tab in your formula editor to see these loop-specific values:
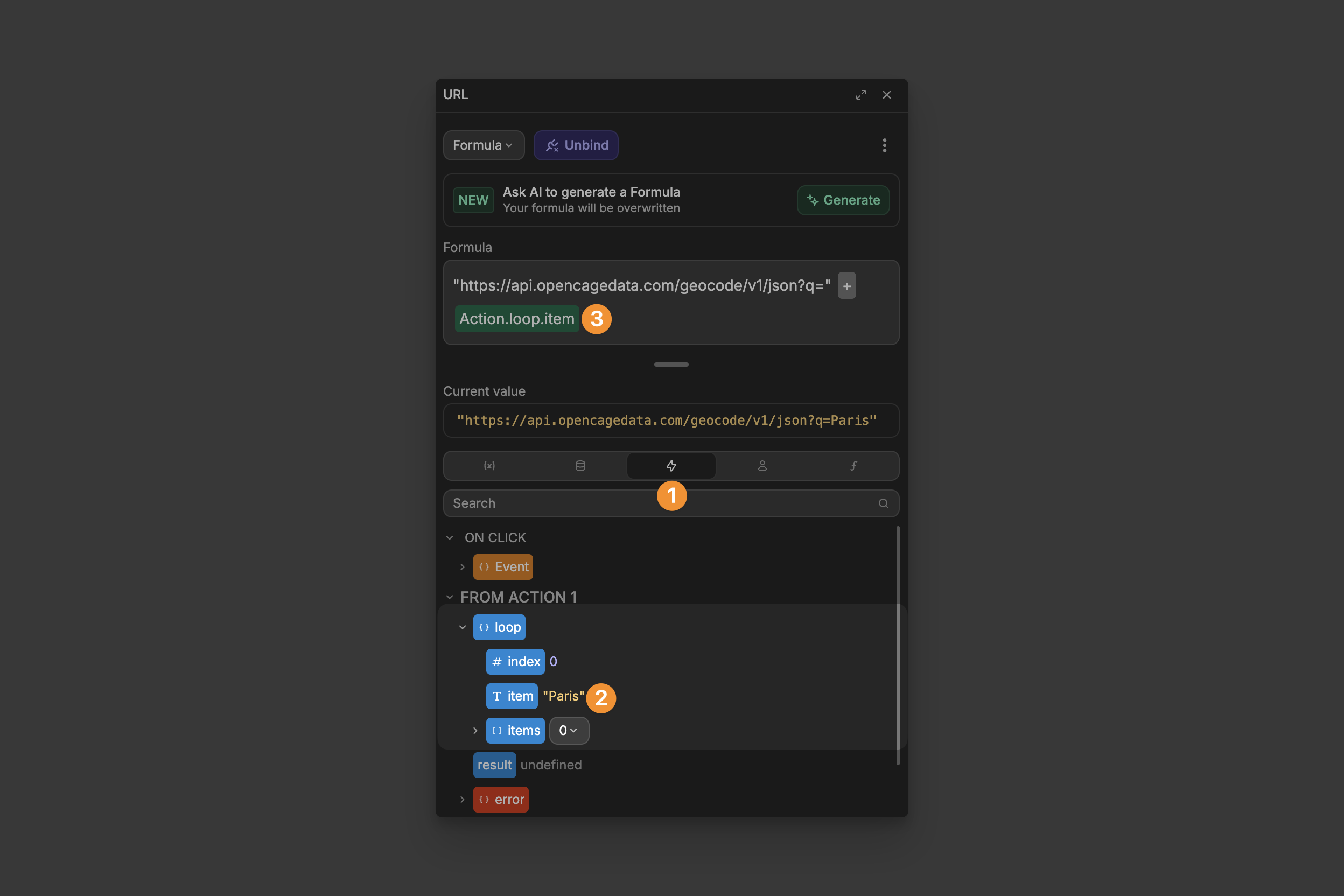
Action.loop.index: The position of the current item in the list (starting at 0)Action.loop.item: The current item being processedAction.loop.items: The entire list of items being processed
TIP
You will only be able to see the available loop information after the loop has ran at least once. After binding your list of data to the loop, you can either test your loop action or test the entire workflow to then be able to access the loop information.
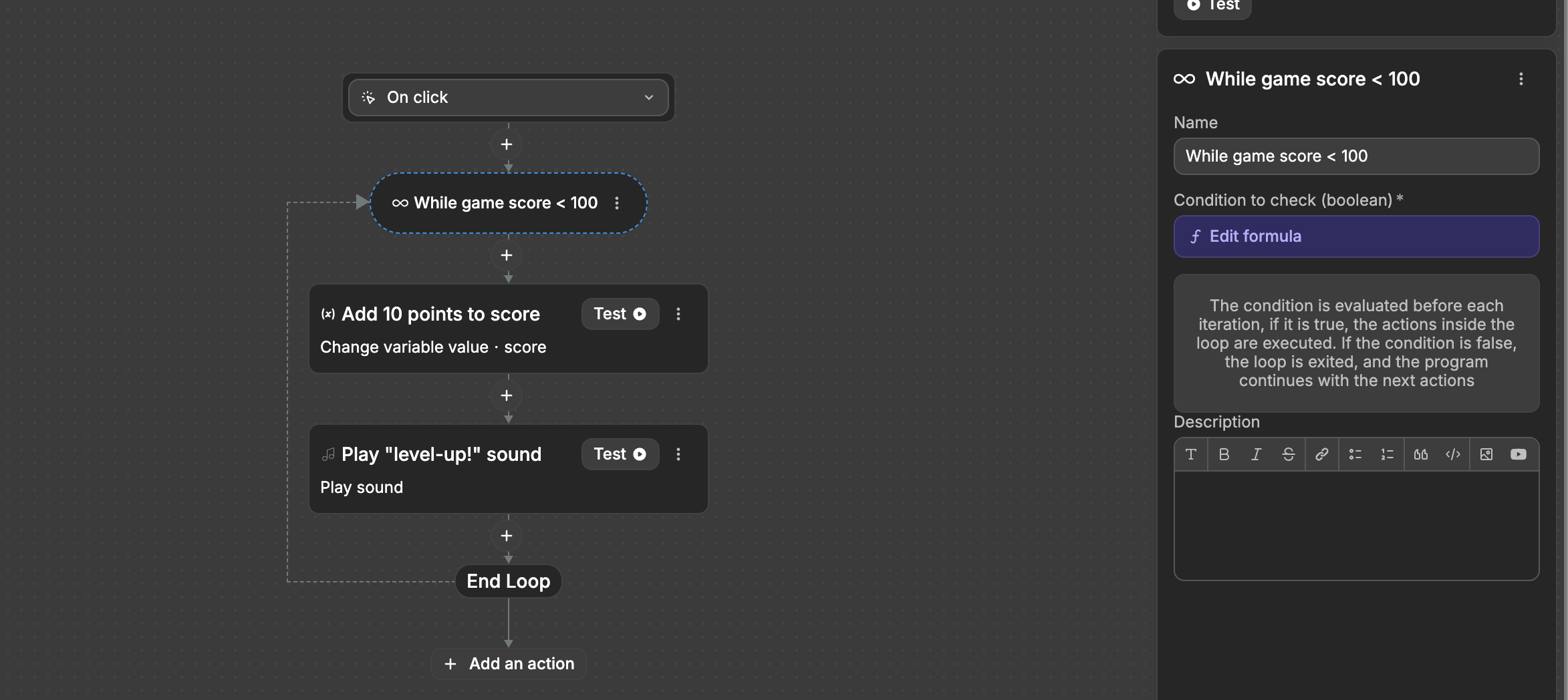
While
A While loop continues running an action as long as a specified condition is true. Unlike an Iterator that processes a list, a While loop checks a condition before each iteration and continues running until that condition becomes false.
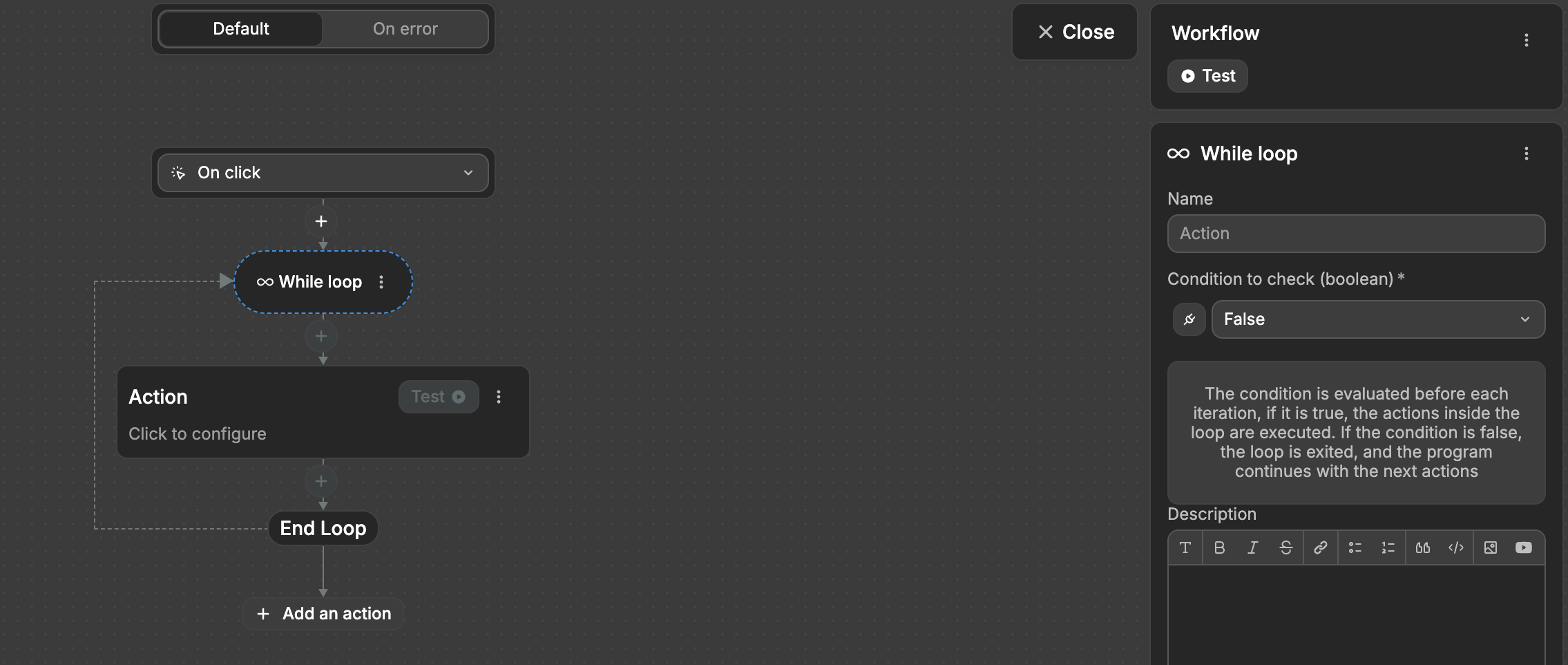
Example:
Imagine you're building a game where a player needs to reach a certain score to advance. Here's how a While loop would work:
- Set a condition (like "score < 100")
- Check the condition
- If true, run the actions inside the loop
- Check the condition again
- Continue this cycle until the condition becomes false
To set up a While loop:
- Add a
Whileloop action to your workflow - Set the condition to check (must be a boolean true/false)
- Add the actions you want to repeat inside the loop
WARNING
Always ensure your condition will eventually become false, or your loop will run indefinitely. If your loop never ends, it could freeze your page or cause poor performance.
Loop Control
Loop control actions allow you to change how a loop executes, giving you more precise control over your workflow. There are three main ways to control loop execution: Break loop, Continue loop, and Pass through condition.
Break loop
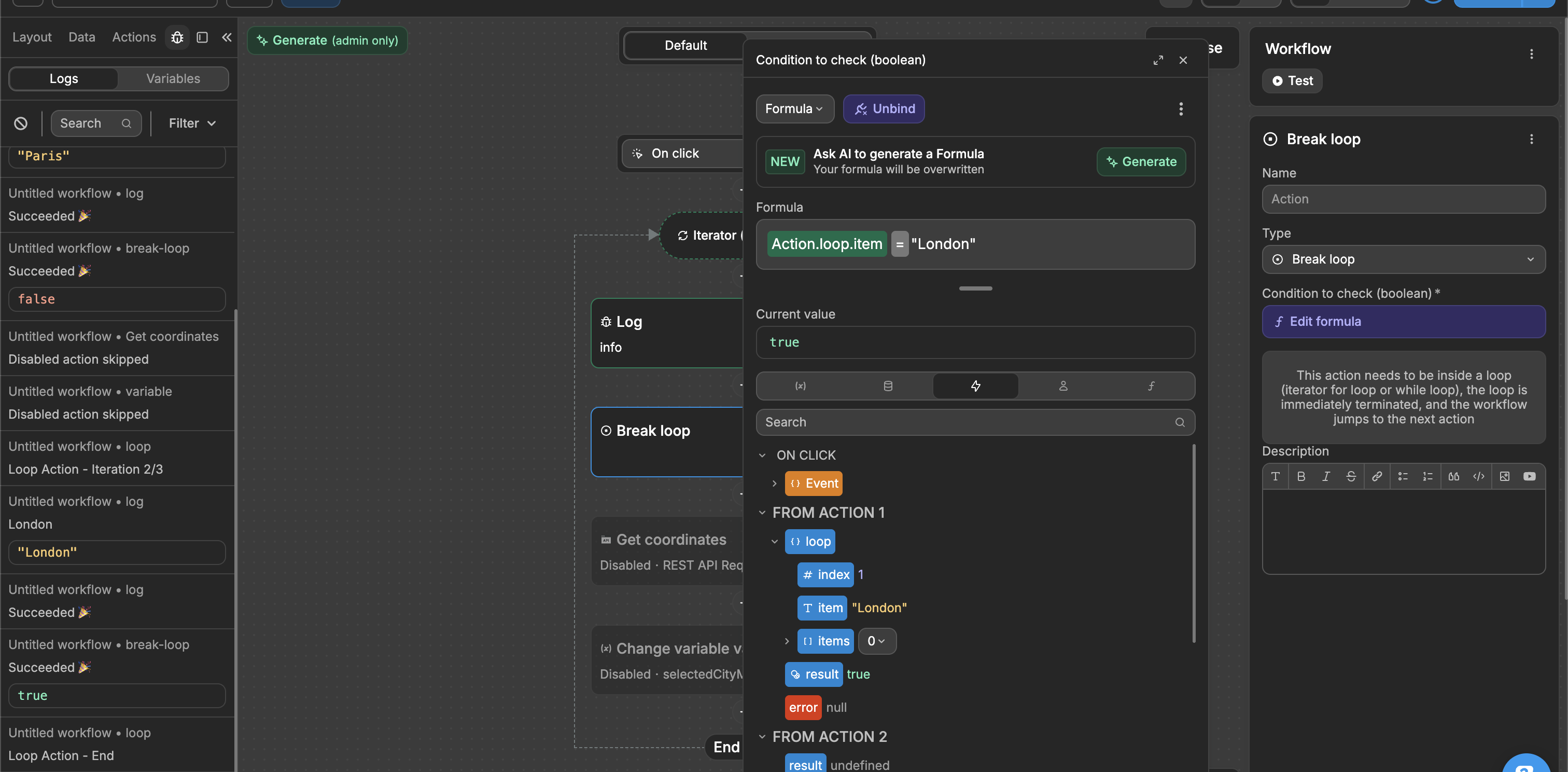
A Break loop action stops the loop immediately when its condition is met. This action only works inside Iterator or While loops and will skip any remaining iterations, continuing with the next action after the loop.
In the example below, we loop through a list of cities ["Paris", "London", "Tokyo"]. Our Break loop condition is set to Action.loop.item = "London". The workflow logs "Paris", then "London", but when it reaches "London" the break condition becomes true and the loop stops. Since the loop ends at "London", "Tokyo" is never logged.
Continue loop
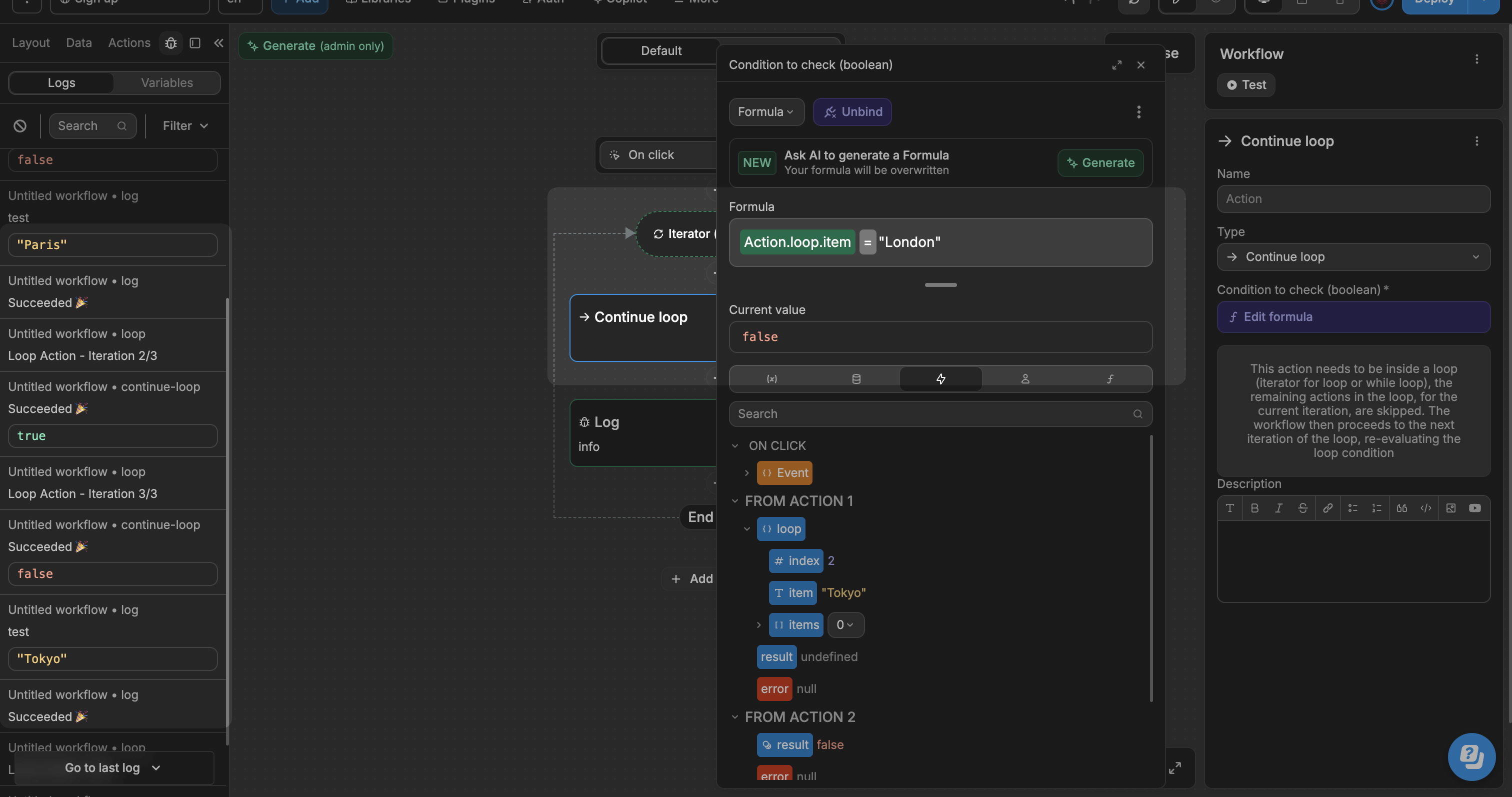
The Continue loop action skips the current loop iteration when its condition is met and moves on to the next item. This action only works inside Iterator or While loops.
In the example below, we loop through a list of cities["Paris", "London", "Tokyo"]. Our Continue loop condition is set to Action.loop.item = "London". The workflow logs "Paris", skips all actions when it hits "London", then processes and logs "Tokyo". As a result, you'll only see "Paris" and "Tokyo" in the logs.
WARNING
Place the Continue loop action at the beginning of your loop actions. Any actions placed before Continue loop will still execute before the skip occurs.
Pass through condition
A Pass through condition controls which actions in your workflow execute. When the condition is false, all following actions are skipped. When true, the workflow continues normally. While Pass through condition works in loops like Continue does, it can also be used anywhere in your workflow as a checkpoint to control which actions should run.
For instance, If a user doesn't have permission (false), all following actions are skipped. If they do have permission (true), the workflow continues executing the next actions.
TIP
- Position your
Pass through conditionbefore any actions you want to conditionally execute. - Actions placed before
Pass through conditionwill always run regardless of the condition. - This action can be used outside loops

