Appearance
Academy
Want to learn how to implement secure user access controls? Check out our Scale your web app course which covers roles, permissions, and best practices for securing your application.
Private pages
Pre-requisite
To make a page private in WeWeb, you first need to have added and configured an authentication plugin.
For authenticated users
Assuming you have added and configured an authentication plugin, you will be able to decide if everybody can access a page or only authenticated users:
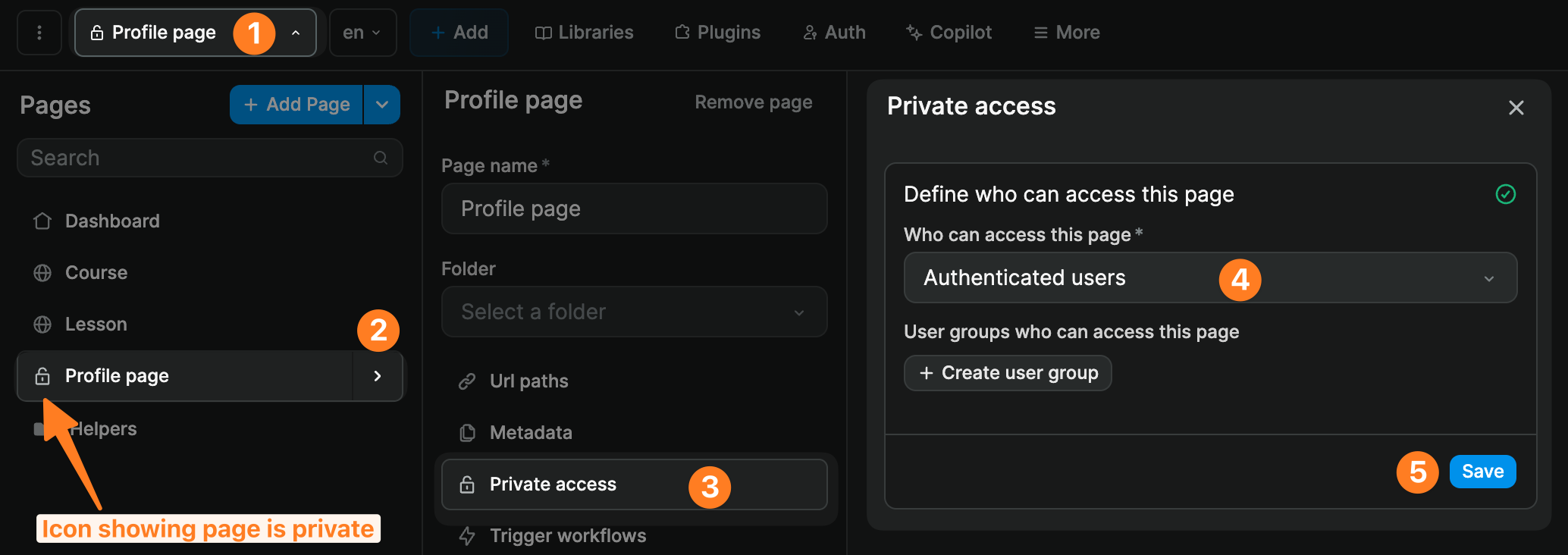
If you choose the Authenticated users option, the page will only be accessible to users that are logged in.
TIP
Inside the WeWeb editor, you will be able to access all pages, including private pages, even if the user is not logged in. This was done to avoid users being stuck when building in WeWeb.
WARNING
When defining redirections in your authentication plugin, make sure you redirect unauthenticated users to a public page. If you redirect unauthenticated users to a page that is only accessible to authenticated users, you'll be creating an infinite loop and your app will crash.
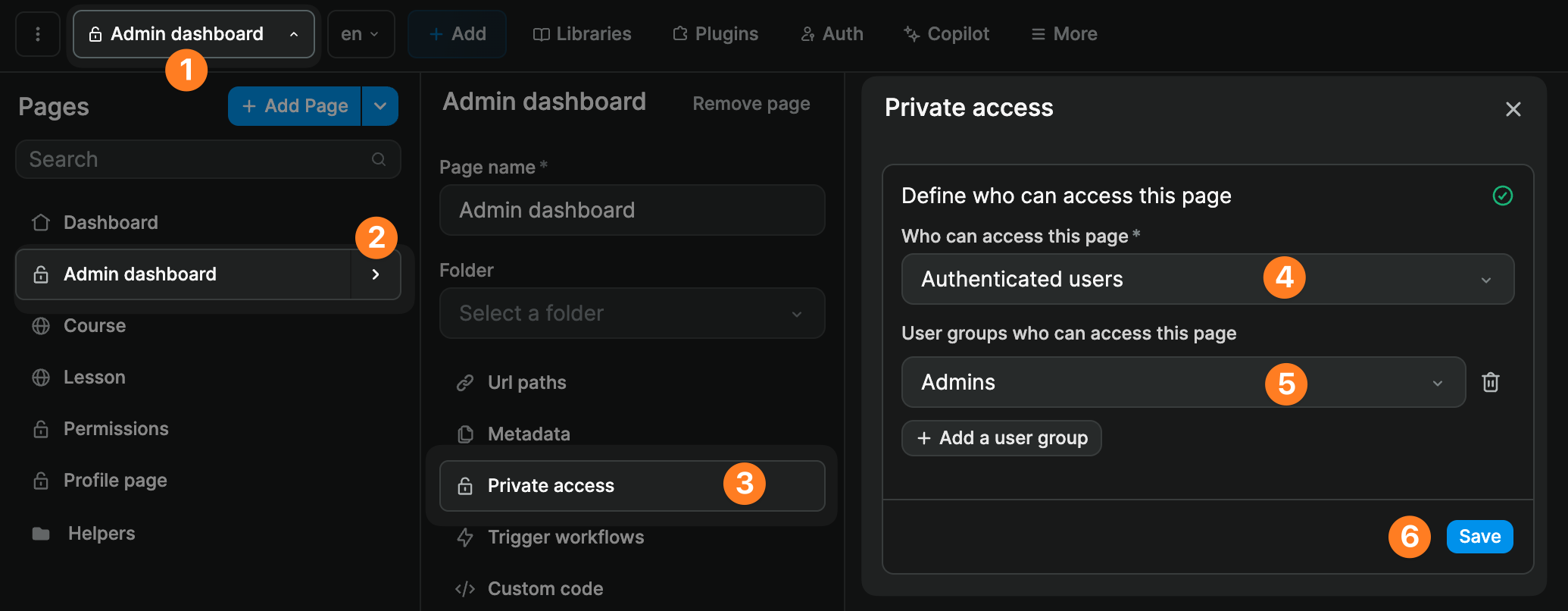
For user groups
If you have defined user roles in your backend and user groups in your authentication plugin, you will also have the option to restrict access to a specific group or groups:
TIP
Inside the WeWeb editor, you will be able to access all pages, including private pages, even if the user is not part of the required user group. This was done to avoid users being stuck when building in WeWeb.
WARNING
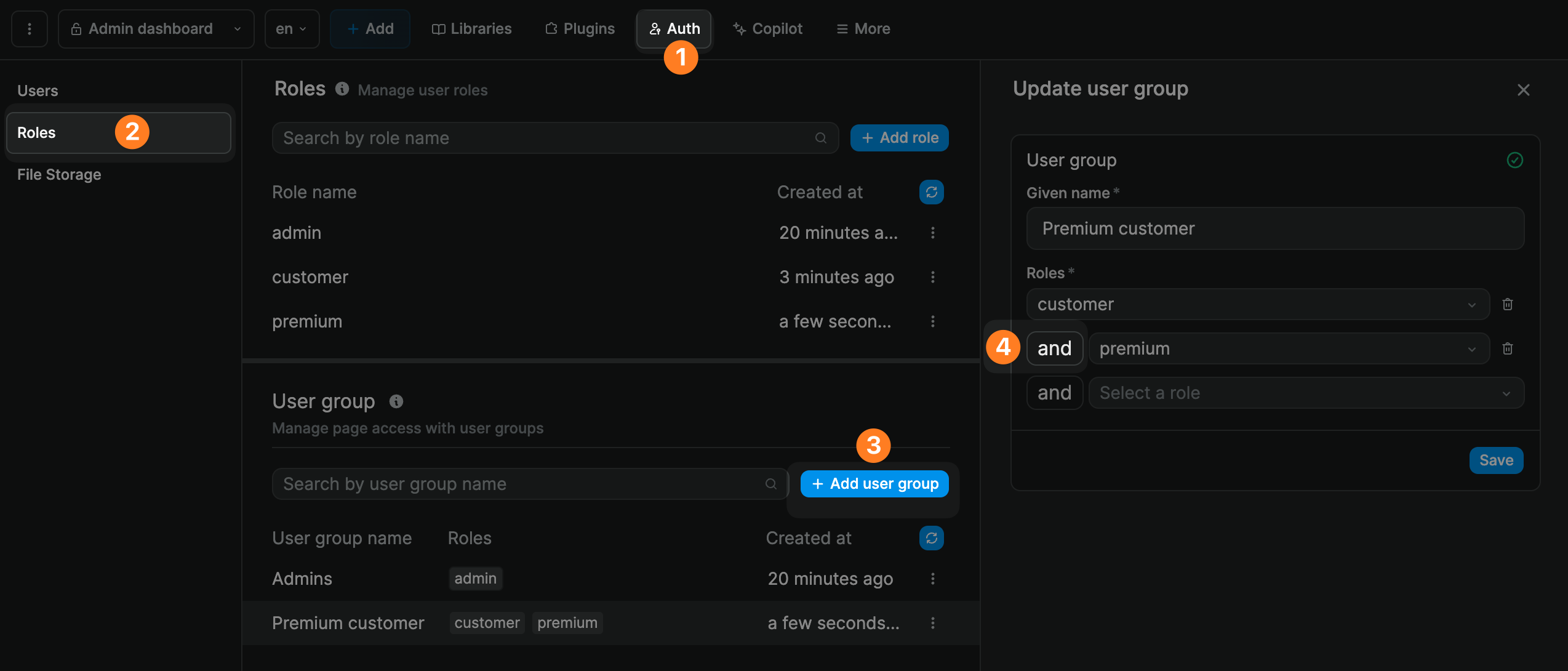
When you add several roles to a user group, a user needs to have BOTH these roles to be part of the user group. It's an AND statement, not OR.
In the example below, the members of the Premium customer user group must have both the Customer and the Premium roles associated with their user profile:
Security
It's important to understand that gating content, making a page private, is more of a UX feature than a security measure.
It is best practice to gate content because, by making a page private in the frontend, you make it clear to the user that they are not allowed to access the content on that page.
However, in web development, security always happens in the backend. To protect your data, you must secure the API endpoints or tables in your backend, even if the page that triggers those calls is private.
In other words, if users need to be authenticated or have a specific role to view or edit data, your backend should have access control checks that ensure that users have the proper authorizations when trying to access or update data.
Learn more about securing your web-apps here:

