Appearance
Select
Supabase is built on PostgreSQL, a database system which uses SQL. SQL is a language for interacting with databases to get, delete, and update data using queries. A query is a command that tells the database what action to perform. In SQL, you can retrieve data from a table using the SELECT statement.
if you run:
sql
SELECT CustomerName, City FROM Customers;This query will:
Retrieve the CustomerName and City columns from the Customers table.
It will return a list of all customer names and their corresponding cities stored in the table.
Adding the Supabase plugin provides several actions for performing various operations, including:
Fetching data with Select
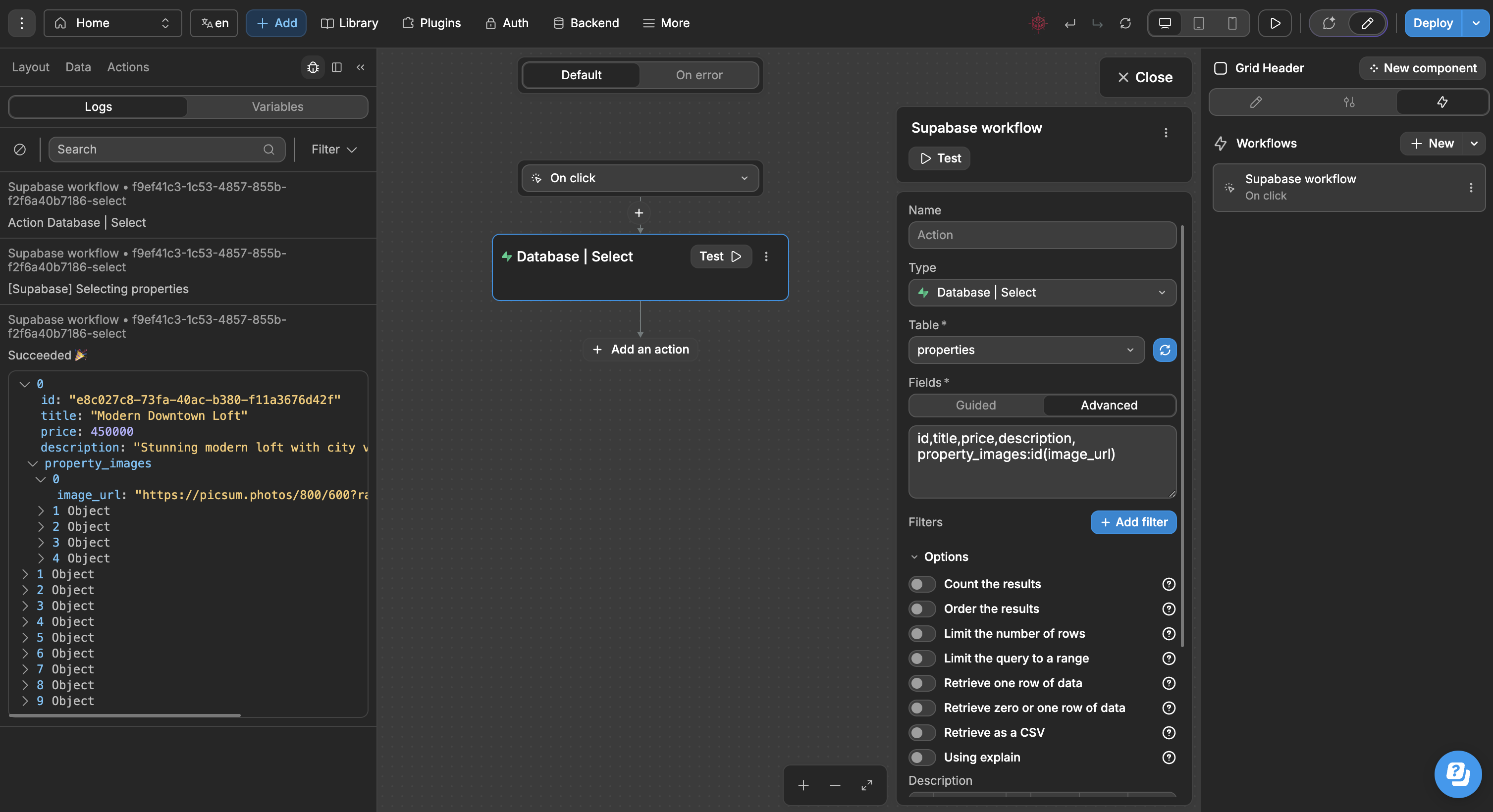
The Database | Select workflow action allows us to get data from our tables. While this is similar to fetching data at the collection level, Database | Select gives us advanced options, namely:
Count the results: get the total number of matching rowsOrder the results: sort data by chosen fieldsLimit the number of rows: return only a specific number of itemsLimit the query to a range: return rows within a range (useful for pagination)Retrieve one row: get exactly one matching recordRetrieve zero or one row: get one record if it exists, nothing if it doesn'tRetrieve as CSV: export data in CSV formatUsing explain: see how the database executes your query (for debugging)
In the example below, we are using the Database | Select action in Advanced mode to retrieve data from the properties and property_images tables:
Filters
To fetch filtered data from Supabase, you can click on Add filter and configure the filter(s) of your choice:
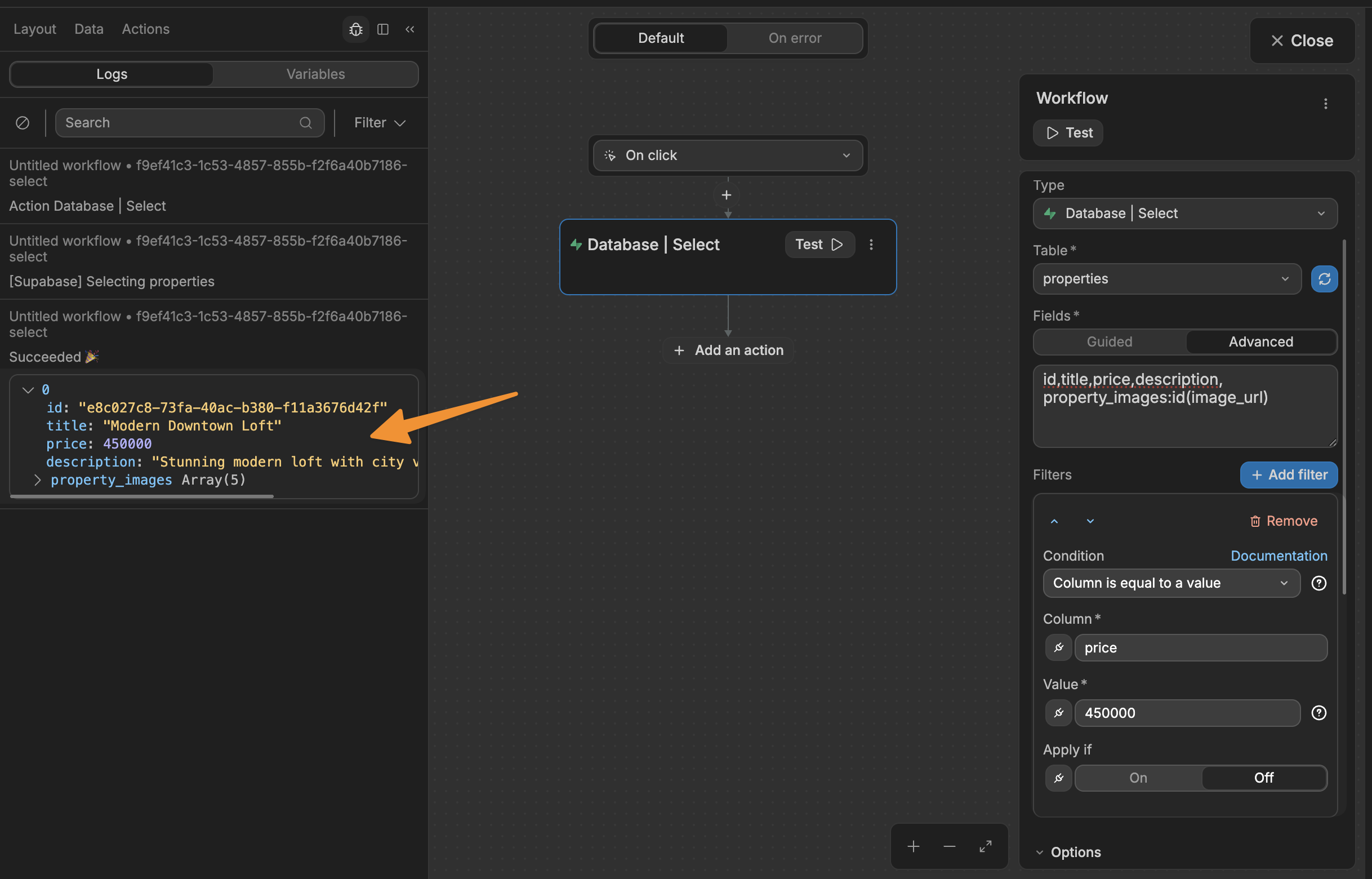
In the example above, we have a simple filter to fetch only the properties where the value in the price column is equal to 45000.
Apply if is a toggle switch that controls whether your filter condition is active or not:
- When
On: the filter (in this case "price = 450000") will be applied to your query - When
Off: the filter is ignored, even though it's set up
Learn more about Supabase filters in their user documentation.
Count results
By default, when you select this option, Supabase will return an object with:
- The number of items returned (the
count), and - The list of items (the
data)
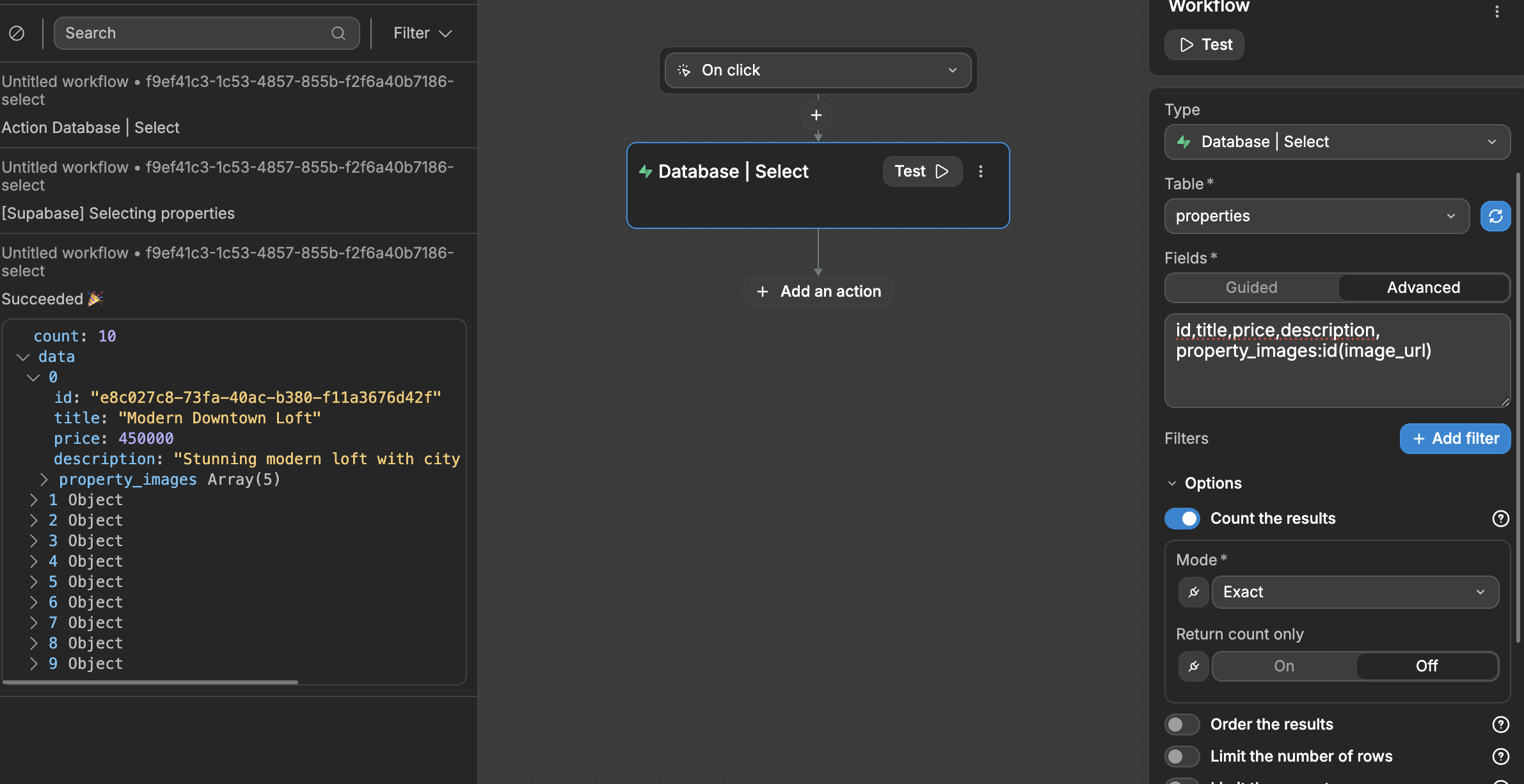
You can choose to return only the count of items without the list of items switching Return count only to On.
Count algorithms
By default, WeWeb will request the Exact count of items to Supabase, but you can ask Supabase to returned the Planned or Estimated count instead.
Exact: counts everything precisely but slowerPlanned: uses pre-calculated numbers, faster but might be offEstimated: usesExactfor small data,Plannedfor large data
TIP
Counting is important in database queries to determine how many records exist in a given context. This is commonly needed in flows like:
- Search results: displaying "Found 237 results" after a search query.
- Analytics & dashboards: calculating total users, sales, or other metrics.
- Conditional logic: deciding whether to show "No items found" or load more data.
Since counting all rows (Exact) can slow down large queries, optimized methods (Planned or Estimated) help improve performance while providing approximate counts.
If you are unsure which count algorithm to choose, Supabase recommends starting with Exact and explore other options when performance becomes an issue.
Learn more about Supabase count algorithms.
Order the results
With this option, you can order the items in ascending or descending order:
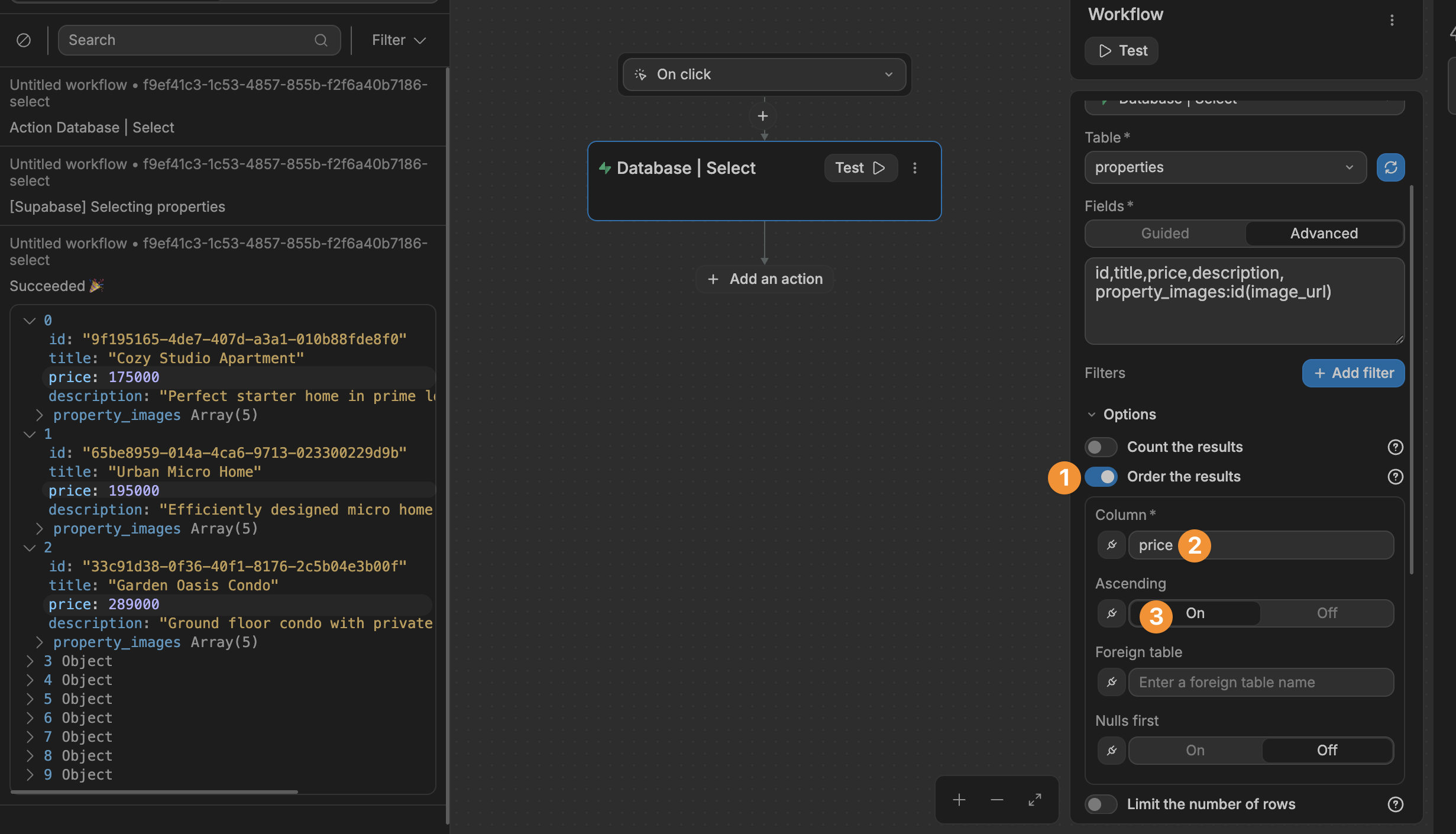
In the example above, the properties are ordered by price, in ascending order. As a result, properties with the lowest price are listed first.
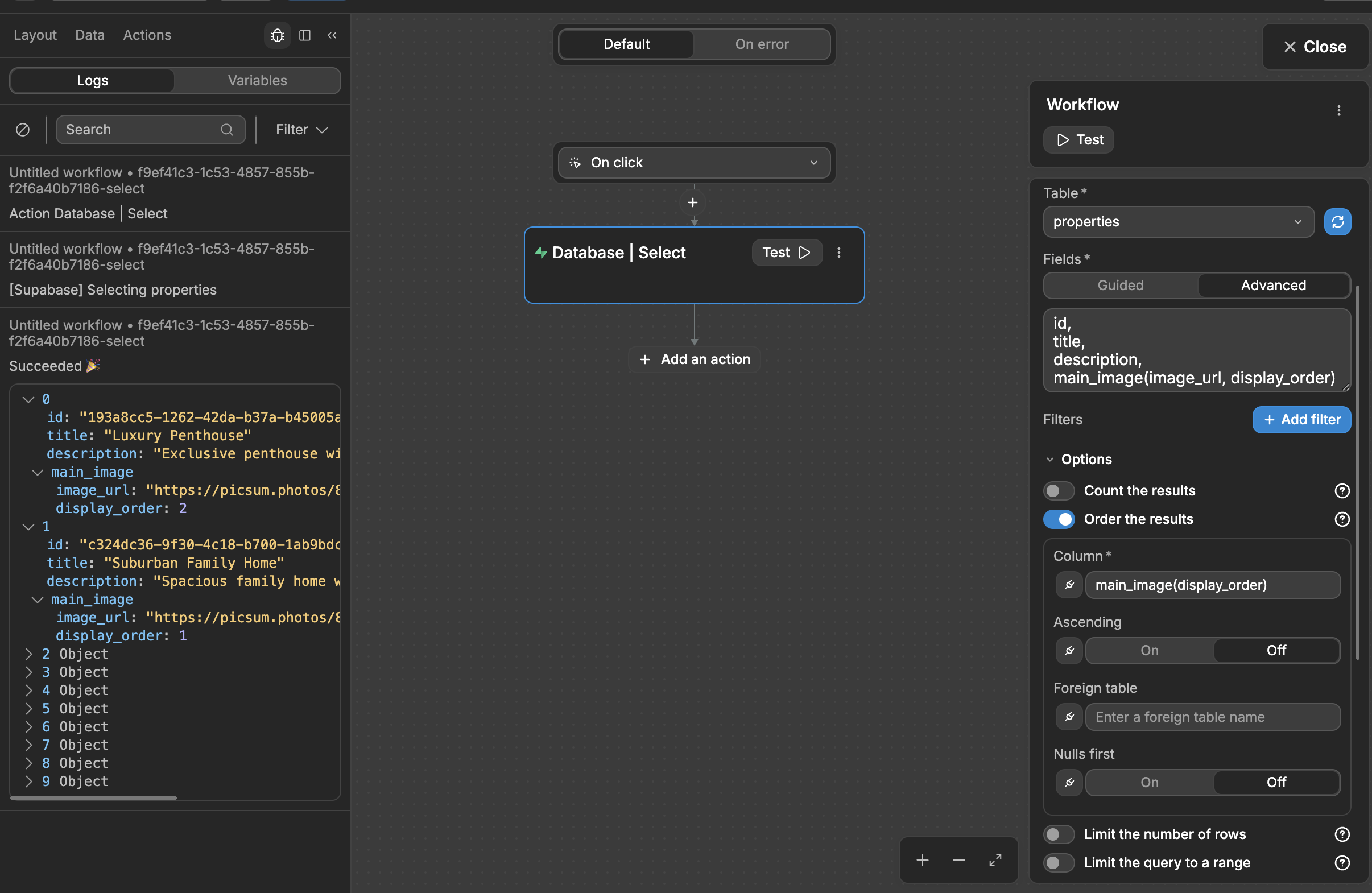
Order by referenced table value
You can order items based on the value of a related field.
For example, in our properties table, we could have a main_image field that references the property_images table.
In the Fields step of our select configuration, we used the Advanced mode to fetch the related image_url and display_order values of each property record. Now, we can order our properties based on the display_order of its main image:
TIP
Nulls first is an ordering option in SQL that determines where NULL values should appear when sorting results.
For example, if you're ordering properties by price and some properties have no price (NULL):
- With
NULLS FIRST: NULL, $450000, $650000 - With
NULLS LAST: $450000, $650000, NULL
WARNING
You can only sort by data from linked tables using Database | Select if you've first specified those linked fields in Advanced mode.
For example, to sort properties by their main image display order, you must first specify property_images:main_image(image_url, display_order) or main_image:main_image(image_url, display_order) in Advanced mode before you can use display_order as a sorting field.
Limit number of rows
With this option, you can limit the number of rows returned by Supabase. In the example below, you can see Supabase only returns 5 items as requested (from index 0 to 4):
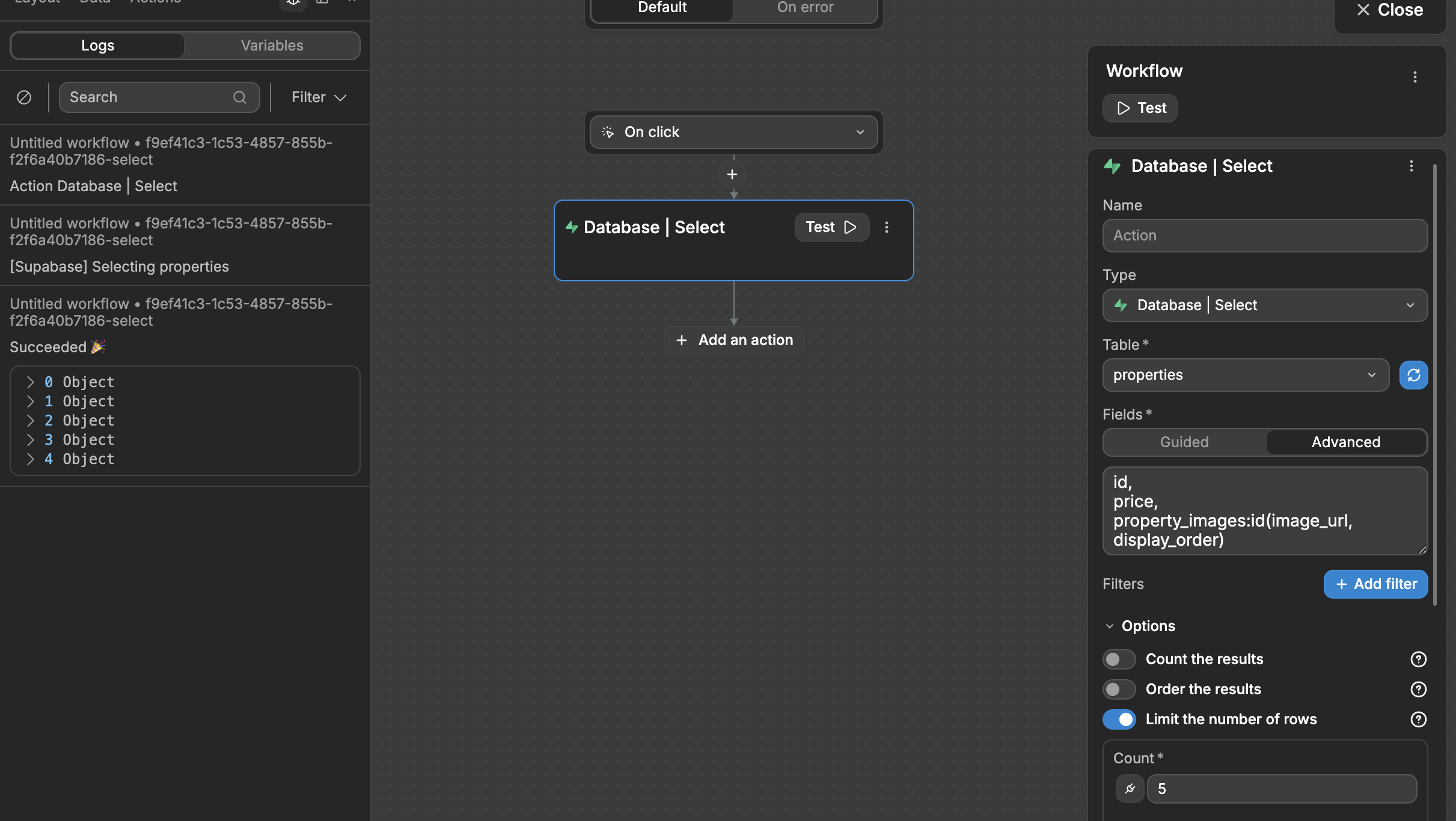
This can be very helpful when setting up custom pagination. You can bind the limit to a variable that is updated when a user clicks on a load more button for example.
TIP
You can also limit the number of rows returned in a field referencing another table.
Learn more about adding a limit on a referenced table.
Limit range
With this option, you can ask Supabase to return a range of items with a start index and end index, for example from 0 to 2:
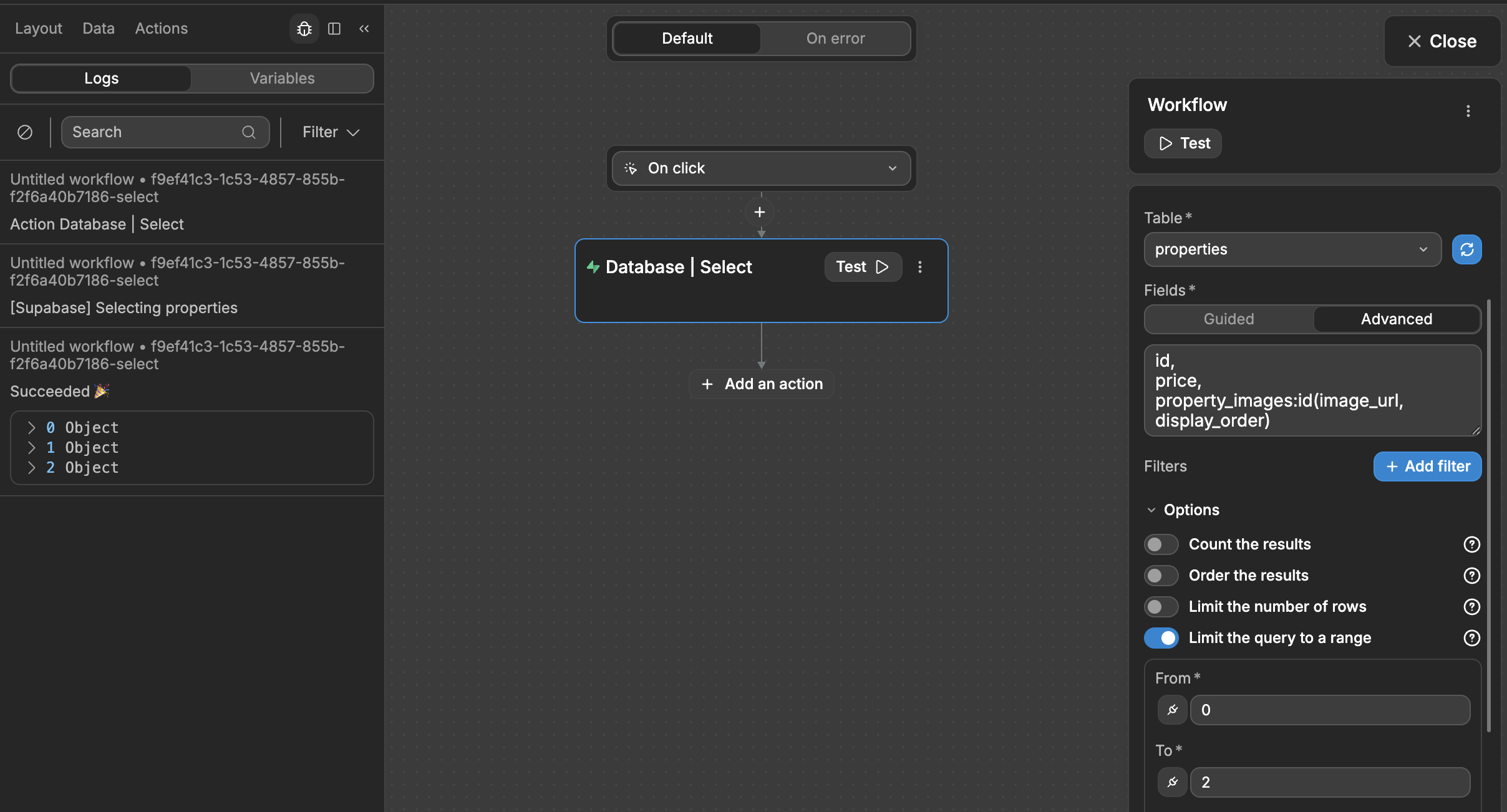
This can be very helpful when setting up custom pagination. You can bind the limit to a variable that is updated when a user clicks on a paginator element for example.
Retrieve one row
Returns first row of the query.
Retrieve as CSV
A CSV is basically just a spreadsheet file - like Excel, but simpler. Getting your Supabase data as a CSV is useful because:
You can open it in Excel or Google Sheets to:
- Look through your data easily
- Make charts and reports
- Share data with team members who don't use technical tools
It's like getting a snapshot of your data that you can:
- Save for your records
- Email to others
- Use in other software
- Print or present
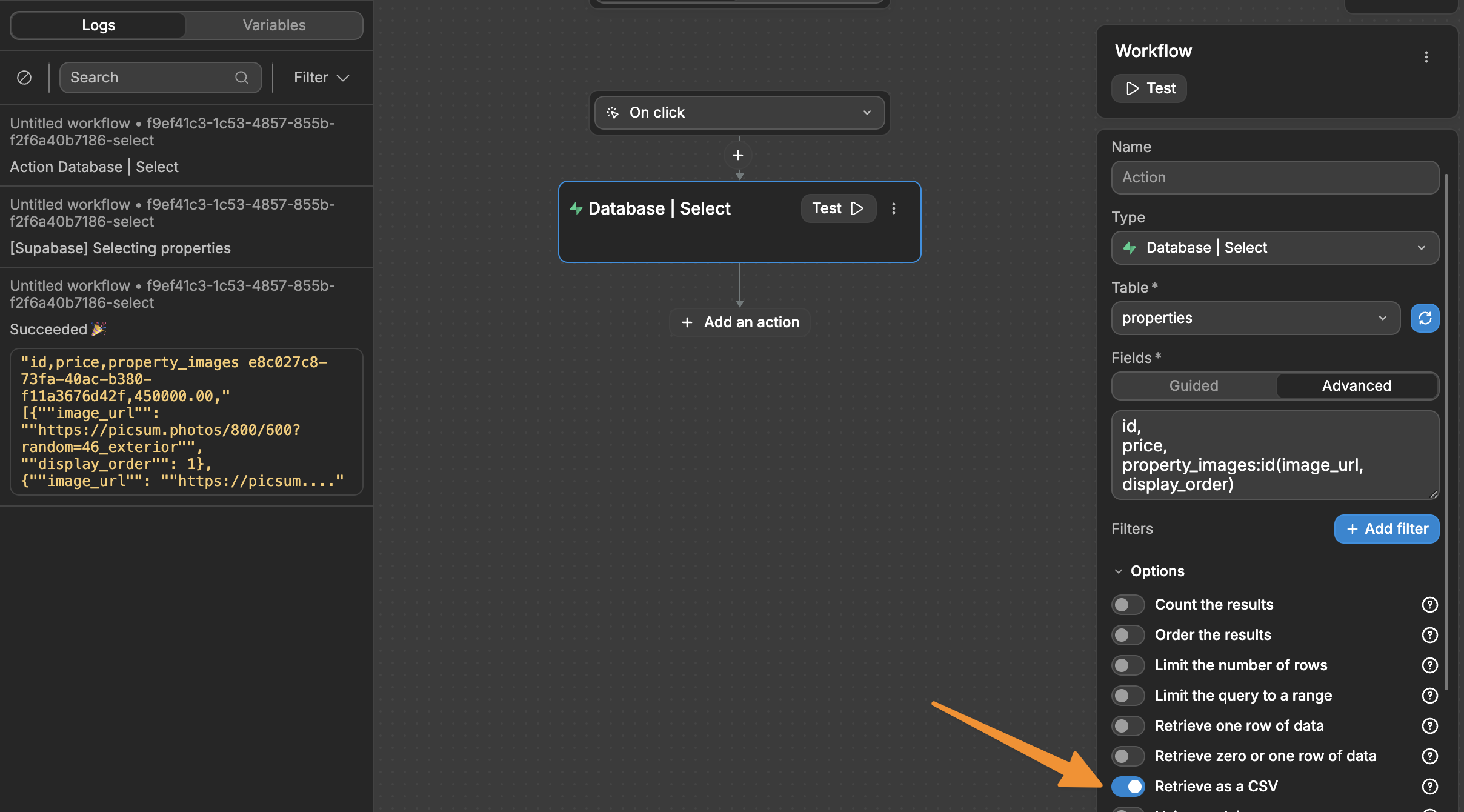
The data retrieved from Supabase as a CSV uses ,, to separate rows.
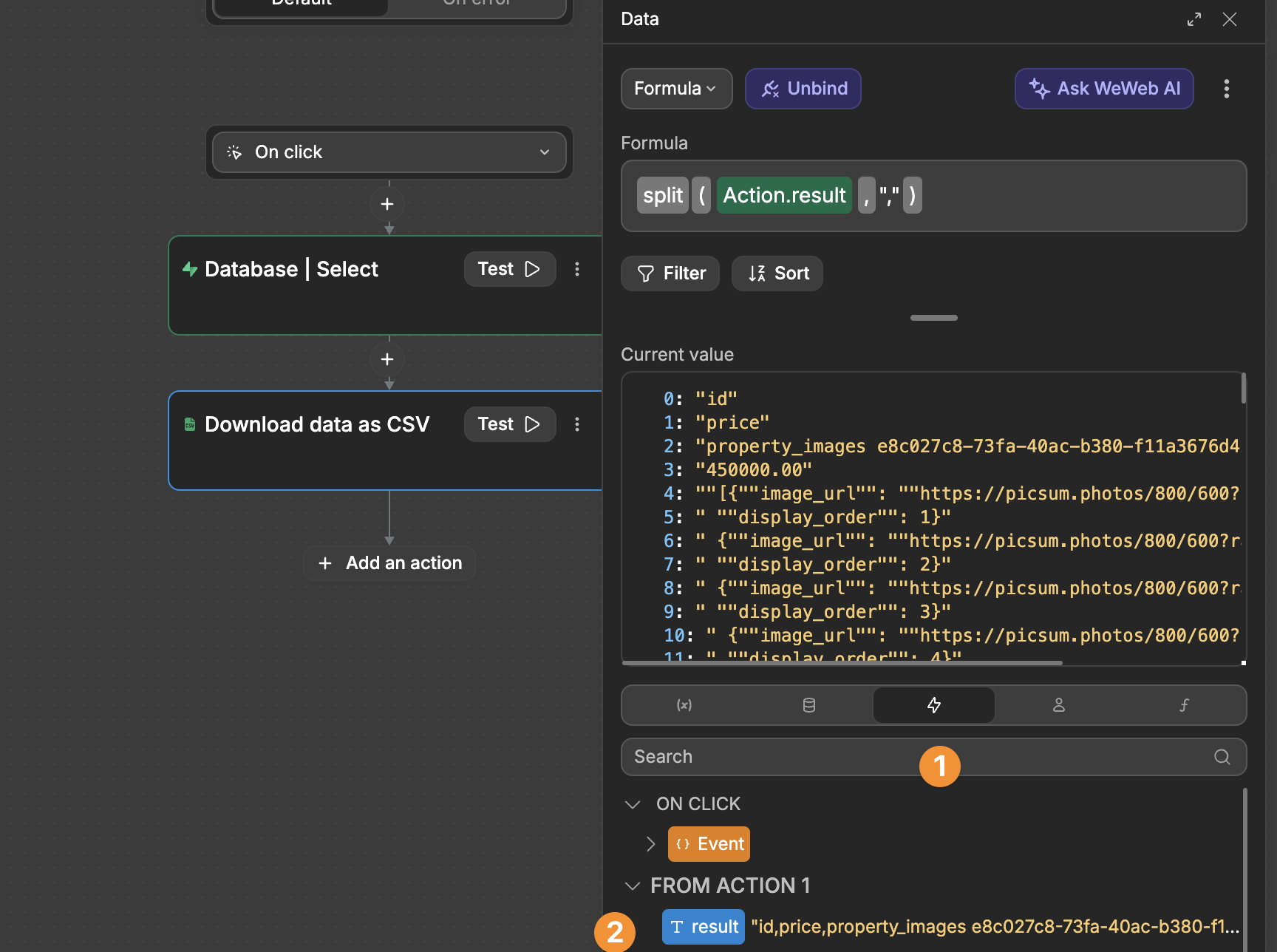
You can download this data in a nicely formatted CSV file by
- Adding the CSV plugin to your WeWeb project,
- Testing your Supabase action first to get a result you can use in the following
Download data as CSVaction - Binding the Supabase action result from the
Eventstab with asplitformula to theDatafield of theDownload data as CSVaction.
Explain
EXPLAIN is a PostgreSQL command that can help you understand and optimize how your queries are performing.
This is an advanced backend feature that we recommend learning through the user documentation of Supabase and its underlying technology PostgreSQL.

