Appearance
Xano request action
When you add the Xano data source plugin to a WeWeb project, it unlocks the Xano Request action in workflows.
Request action
The Xano Request action in workflows allows you to make requests to the endpoints of the Xano instance you configured in WeWeb's Xano data source plugin:
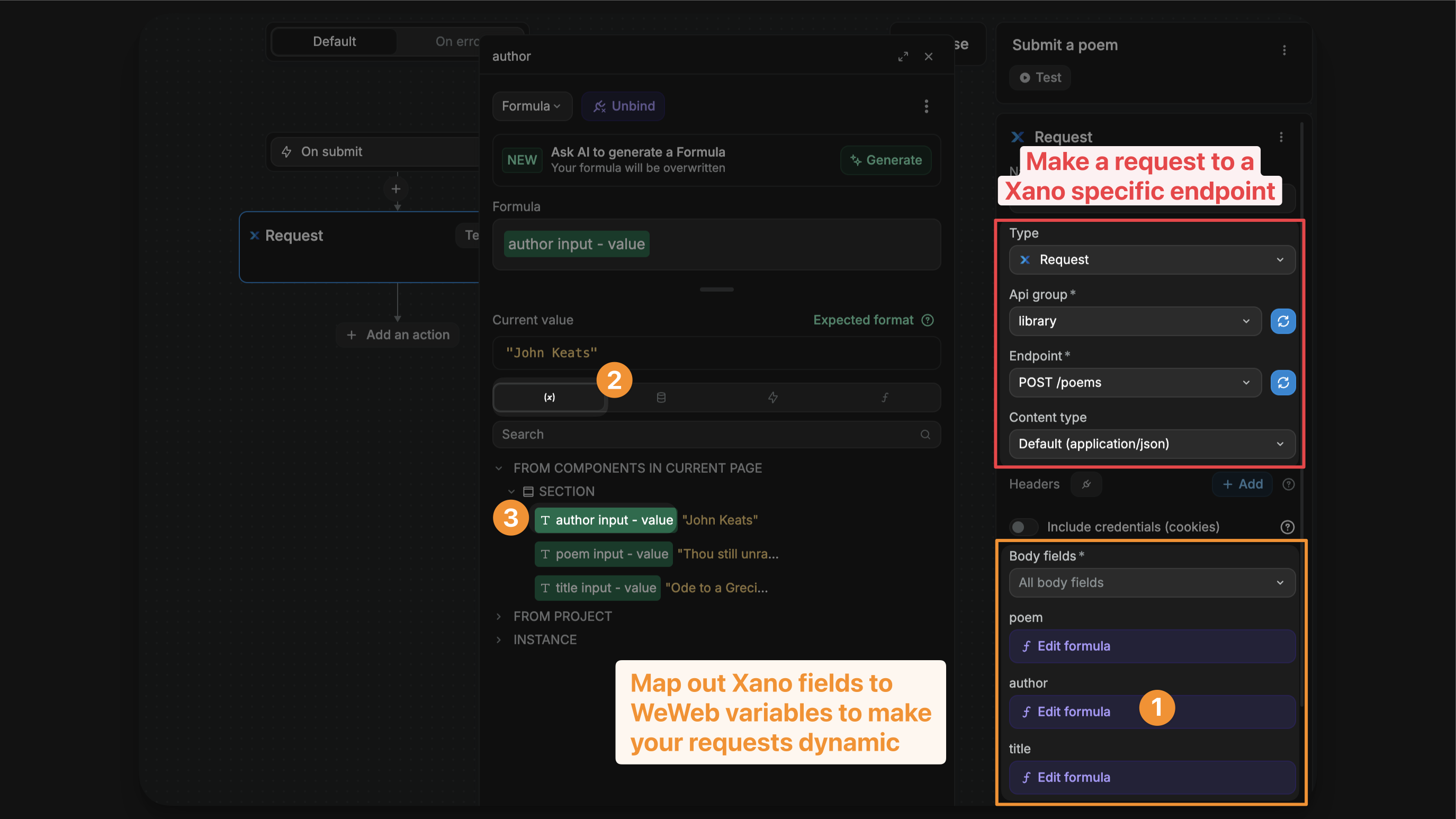
In the example above, you can see that we are configuring a call to:
- the
POST poemsendpoint, - in the
libraryAPI group of our Xano instance.
This endpoint includes 3 inputs – poem, title, and author – which I bound to input variables from my WeWeb project.
As a result, the values I send to Xano will vary based on the values in my WeWeb variables.
Using component variables
The Xano Request action can access variables from WeWeb components, making it particularly useful for interactive features like AI chat components, dynamic forms, and real-time applications.
Accessing component data
When configuring your Xano request, you can bind endpoint inputs to:
- Page variables: Global variables available throughout the page
- App variables: Variables accessible across your entire application
- Component variables: Variables specific to individual components on your page
Component variables are especially valuable for:
✅ AI chat implementations: Bind user input from chat components directly to AI endpoints ✅ Dynamic forms: Use form component data to update records in real-time ✅ Interactive elements: Connect component states to backend operations ✅ Real-time updates: Stream component data to Xano for live processing
Example: AI chat component
For an AI chat component, you might have:
- A
messageInputcomponent variable containing the user's current message - A
conversationHistorycomponent variable storing previous messages - A
streamResponsecomponent variable for receiving AI responses
You can bind these component variables directly to your Xano AI endpoint inputs, enabling seamless communication between your frontend components and backend AI processing.
TIP
Component variables are automatically available when configuring Xano requests. Simply select the component variable from the binding menu when setting up your endpoint inputs.
Streaming
Streaming lets your app receive data in small pieces instead of waiting for the full response. It’s ideal for chat-style experiences and long tasks where you want to show progress. For tiny or instant responses, a regular request is simpler.
If you wish to copy the endpoint used in the video above, the snippet for it can be found here.
Pre-requisites
Set up your Xano endpoint to stream:
- create an endpoint and inside the settings of the endpoints set its
Response typetoStream - prepare a list of data to send in pieces (for a quick test, make an array variable of words)
- add a
For eachloop to iterate over the list - inside the loop, use
Streaming API responseto send the current item - optionally add a short
Sleepstep to slow the demo so the stream is visible
EXTERNAL API REQUESTS
If you wish to make an external API request inside your Xano endpoint, make sure to use the Streaming API request action in Xano.
Request settings in WeWeb
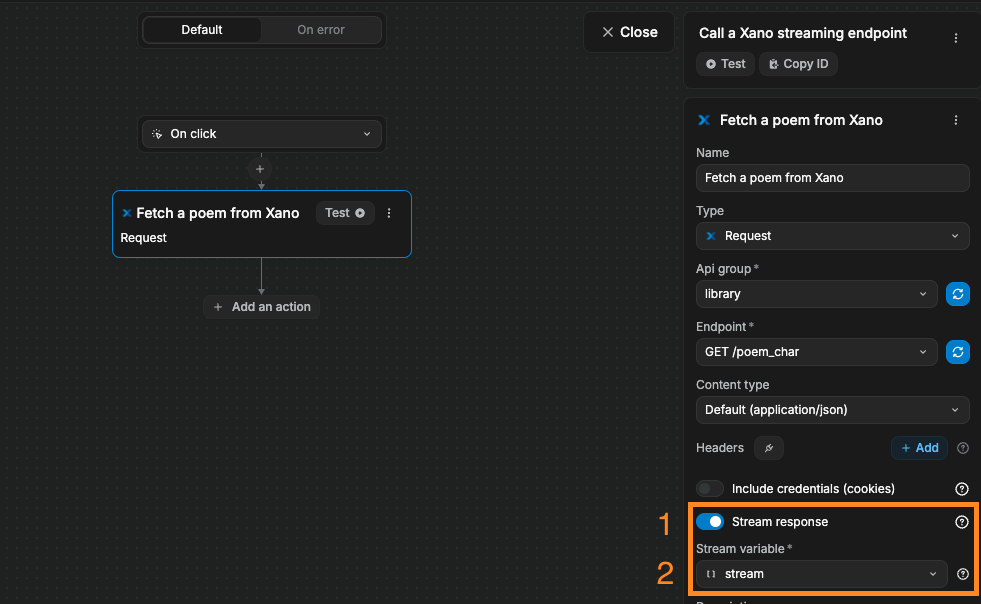
To receive a streaming response from Xano in WeWeb, you'll need to trigger a standard Xano Request action in a workflow and ensure two things:
- The option
Stream responseis enabled. - You've selected an array variable in your project where you wish to store the streaming response.
When we test the action, we can see our stream variable being updated line by line:
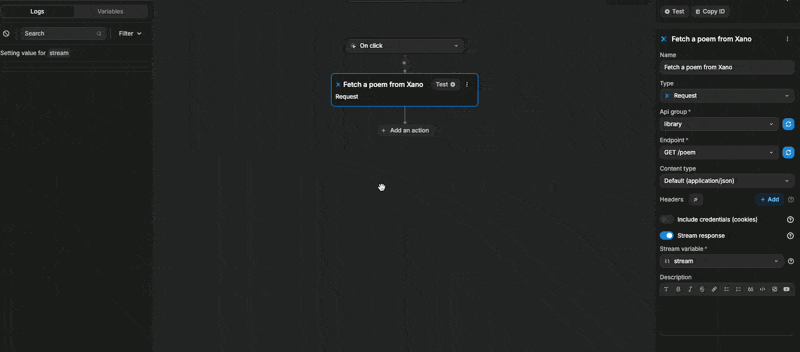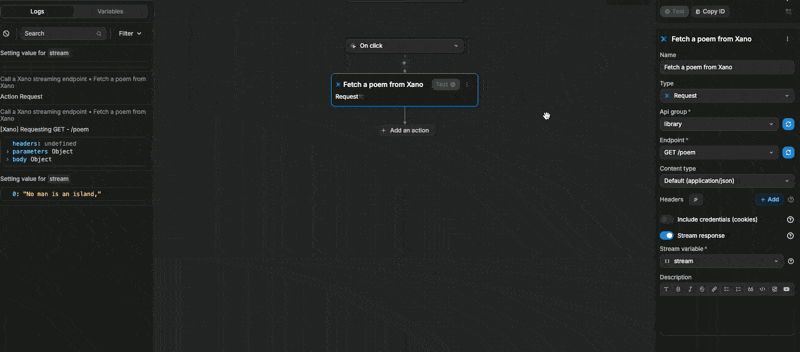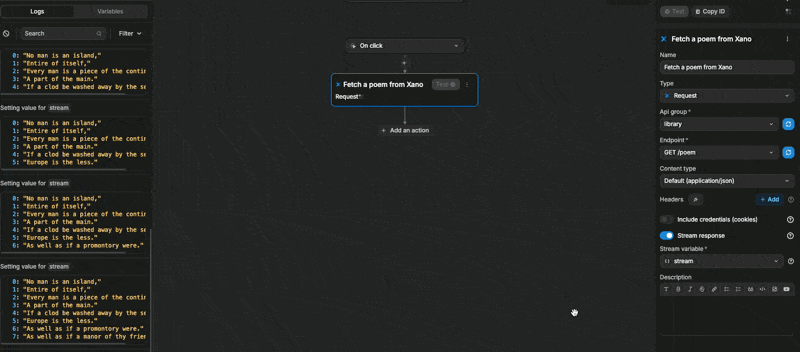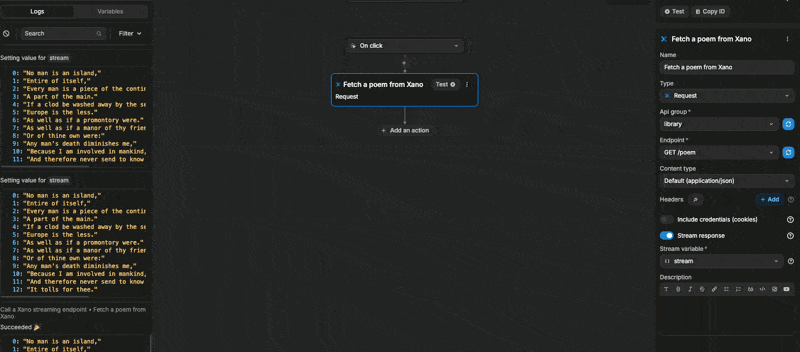
This is because, in Xano, our variable was an array of lines. When we looped through the variable, each item was a line:
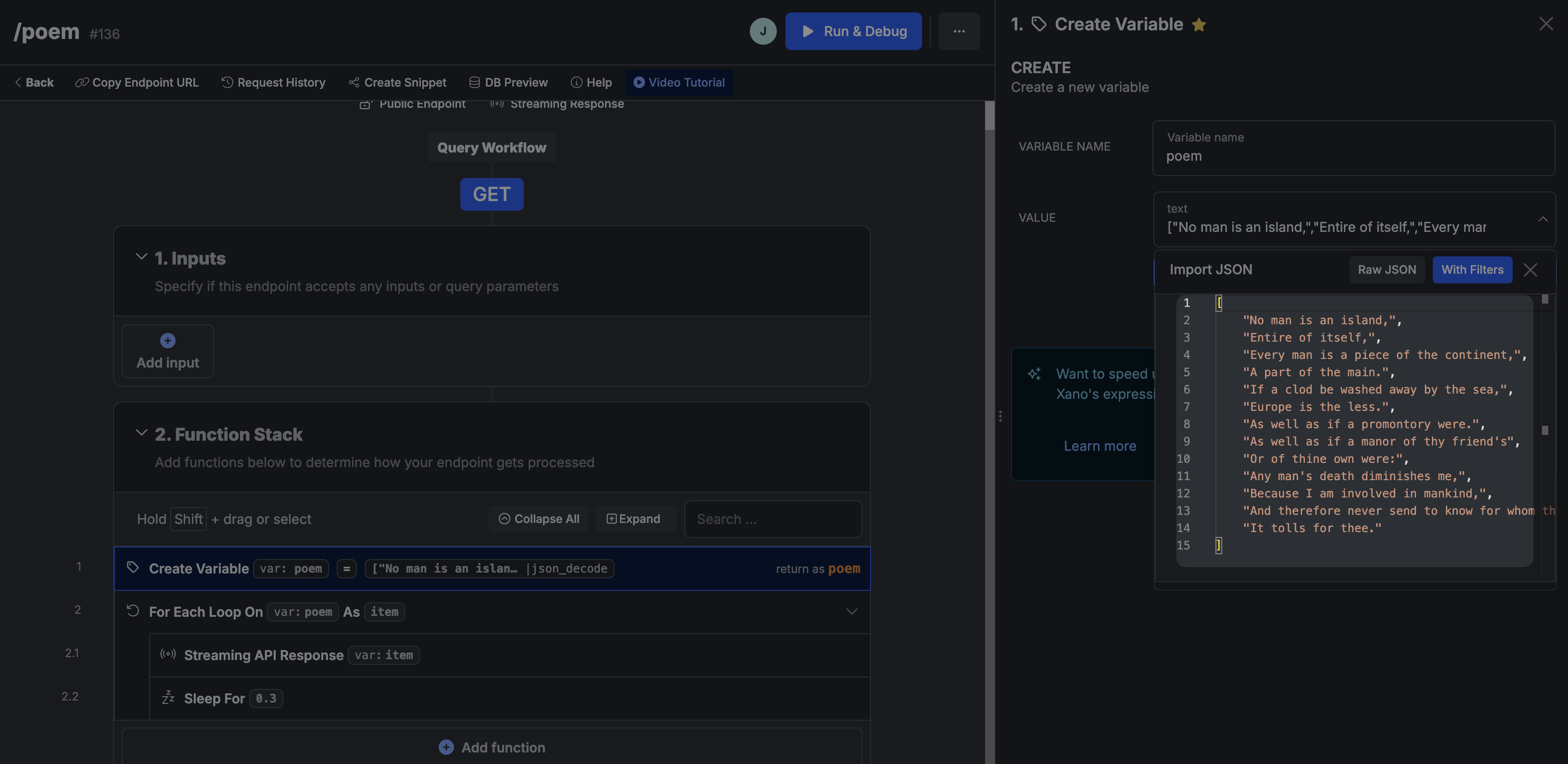
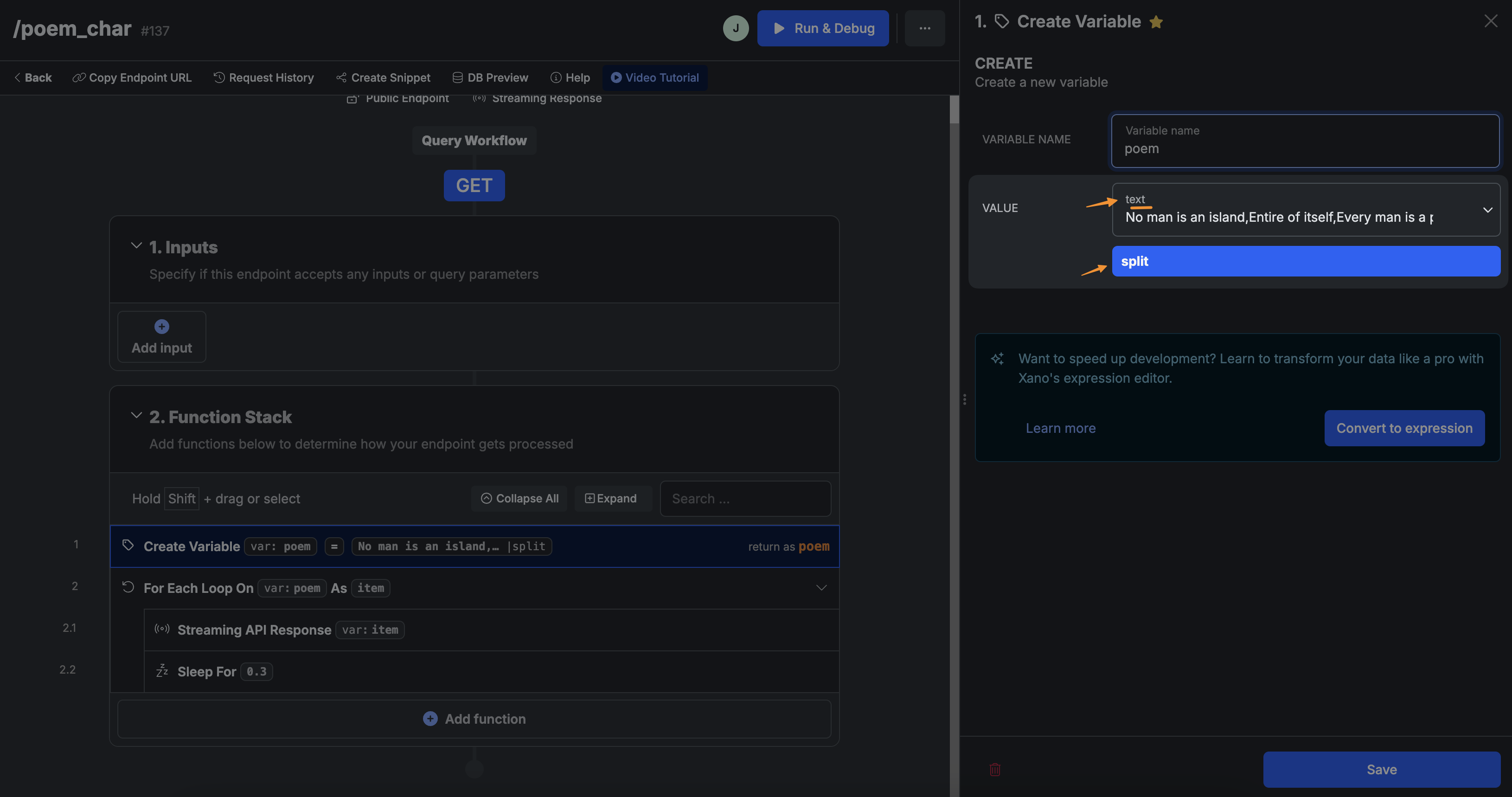
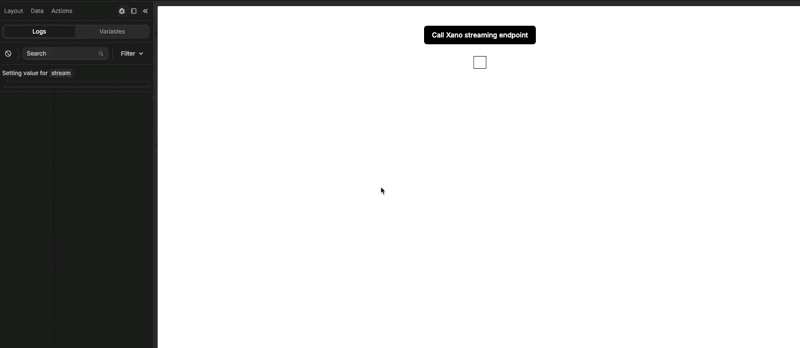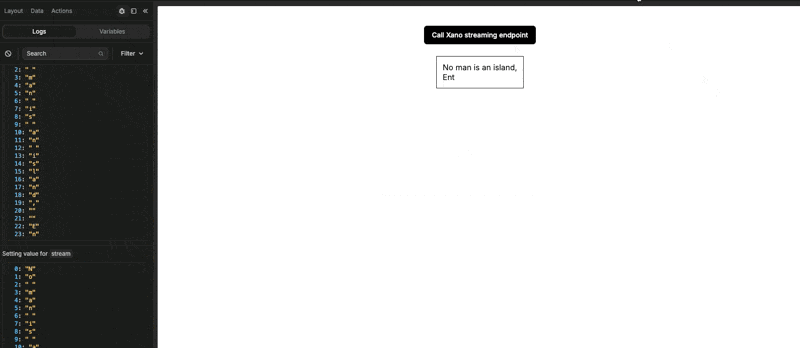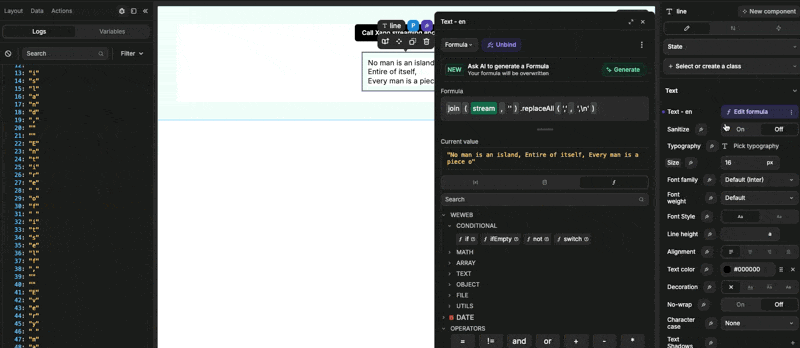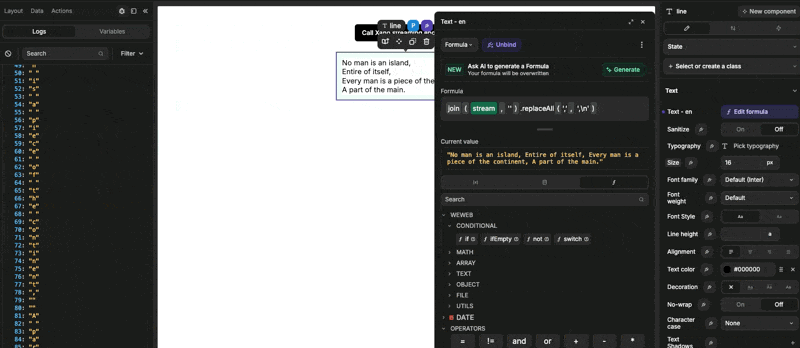
If we wanted to stream the response character by character, we would need to change the function stack of our Xano endpoint so each item is a character.
In the example below, instead of having an array variable in Xano formatted as a raw JSON, we have a strong variable and applied a split function to return the text as an array of character:
Here's what it would look like in action:
WARNING
Your Xano endpoint must stream its response. WeWeb cannot create a stream from a non‑streaming endpoint or from an external API that does not support streaming.
FORMATTING STREAMED RESPONSE
Depending on the payload your endpoint sends, you may need to format the stream before showing it in the UI. Simple cases can be handled by joining an array of strings. For structured chunks (objects), extract only the new content before displaying it.

